KIOSK Banking: A Gateway to Financial Inclusion
In today’s fast-paced world, the traditional banking sector is constantly evolving to cater to the needs of individuals from various walks of life. While urban areas enjoy the privileges of well-established banking networks, rural regions often face a scarcity of financial institutions. KIOSK banking, a novel concept, has emerged as an efficient and scalable solution to extend banking services to the underserved segments, primarily in rural and semi-urban areas.
What is KIOSK Banking?
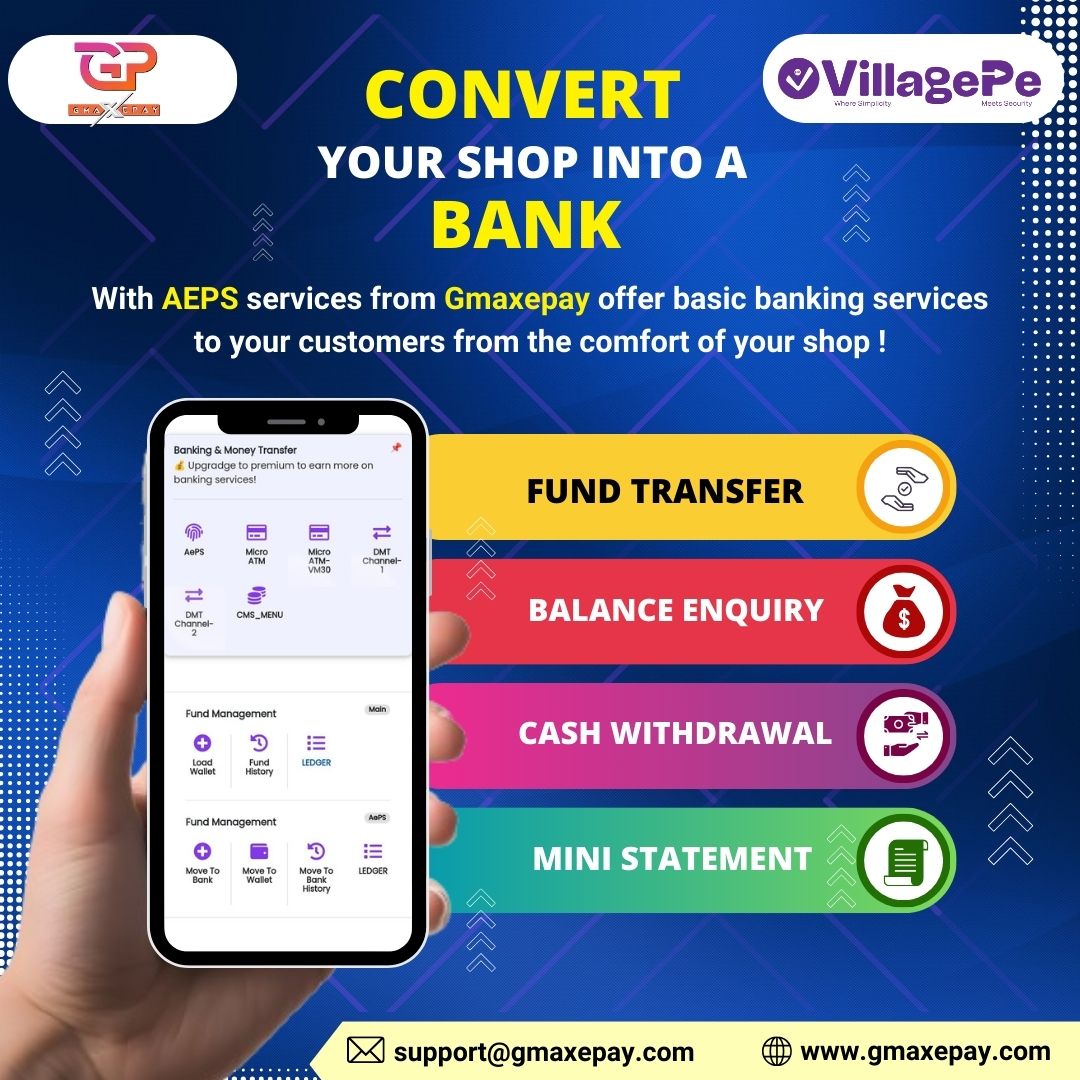
KIOSK banking is a model introduced by several banks, especially public sector banks in India, to ensure financial inclusion for the unbanked population. It involves setting up small, self-service terminals or KIOSKs in remote areas, often in collaboration with local shop owners or businesses. These KIOSKs function as mini bank branches, enabling users to access basic banking services such as opening accounts, cash deposits and withdrawals, fund transfers, balance inquiries, and more.
The prime objective of KIOSK banking is to bridge the gap between formal banking systems and those without access to it, including farmers, daily wage workers, and small-scale entrepreneurs. This model also helps reduce operational costs for banks, as KIOSKs are easier and cheaper to maintain than traditional brick-and-mortar branches.
Its Benefits
1. Financial Inclusion:
One of the most significant advantages of KIOSK banking is its role in promoting financial inclusion. By establishing KIOSKs in remote areas, banks are bringing financial services to the doorsteps of people who previously had limited or no access to banking facilities.
2. Low Operational Costs:
For banks, setting up a full-fledged branch in every village is both financially and logistically unfeasible. KIOSK banking allows banks to extend their services at a fraction of the cost, with lower infrastructure and staffing requirements.
3. Convenient and Time-Saving:
Customers no longer need to travel long distances to access banking services. KIOSK banking allows individuals to perform basic banking transactions at a location near their homes or workplaces. This is especially beneficial for people living in remote or rural areas.
4. Employment Generation:
KIOSK banking centers often partner with local entrepreneurs or business owners, providing them with additional revenue streams. This model fosters employment and boosts small-scale business growth in rural regions.
5. Real-Time Transactions:
KIOSK banking terminals are equipped with real-time systems that allow for seamless and instant transactions, ensuring that customers experience minimal delays in their banking activities.
6. Promotes Digital Literacy:
As people begin using KIOSKs for their banking needs, they become more familiar with digital systems. This helps in spreading digital literacy in rural areas, encouraging the population to adapt to modern technology.
Process of KIOSK Banking
1. Partnering with Business Correspondents (BCs):
Banks collaborate with business correspondents, who are individuals or entities representing banks in providing banking services. These BCs are typically local shop owners, Common Service Centers (CSCs), or small entrepreneurs. The selected BC acts as a bridge between the bank and the customers in the locality.
2. Setting Up the KIOSK:
Once the bank partners with a BC, a KIOSK is set up in their premises. The KIOSK is equipped with a computer, biometric scanner, printer, and internet connection to facilitate transactions. The BC is provided with the necessary software and training to operate the KIOSK smoothly.
3. Account Opening and Other Services:
The KIOSK banking process allows users to open a basic savings account with minimal documentation, often requiring just an Aadhaar card or other basic identification. The KIOSK also facilitates:
- Cash Deposits: Customers can deposit money into their accounts through the KIOSK.
- Cash Withdrawals: Customers can withdraw money using their account details and biometric verification.
- Balance Inquiries: Customers can check their account balances and mini-statements.
- Fund Transfers: Money transfers between accounts are possible via the KIOSK system.
- Payments: Utility bill payments, mobile recharges, and other financial transactions can be done through the KIOSK.
4. Biometric Authentication:
One of the key components of KIOSK banking is the use of biometric authentication, especially for transactions like withdrawals and transfers. This makes the system highly secure, reducing the chances of fraud or misuse.
5. Real-Time Reporting:
The KIOSK banking system is linked to the bank’s core banking system (CBS), ensuring that all transactions are updated in real-time. This not only enhances transparency but also builds trust among users, as they can immediately verify their transactions.
Eligibility Criteria for KIOSK Banking
For Customers:
KIOSK banking is designed to cater to individuals from all walks of life, particularly those in rural and semi-urban areas. The primary eligibility criteria include:
- Basic Identification Documents: Aadhaar card, PAN card, or voter ID are typically required to open an account at a KIOSK.
- Resident of a Rural or Semi-Urban Area: While KIOSKs are mostly located in remote regions, anyone from the vicinity can use these services.
- No Need for Prior Bank Accounts: Even individuals who do not hold a bank account can easily open one through KIOSK banking.
For Business Correspondents (BCs):
Individuals or small businesses interested in becoming business correspondents for KIOSK banking must meet certain criteria:
- Minimum Education: A high school education is often required to ensure basic literacy and numeracy skills.
- Financial Background: BCs should not have a history of defaulting on loans or any financial irregularities.
- Local Business or Shop: BCs need to have an existing business or a shop that can serve as a KIOSK banking point.
- Training and Certification: The potential BCs undergo training provided by the bank to familiarize them with KIOSK operations, security protocols, and customer service.